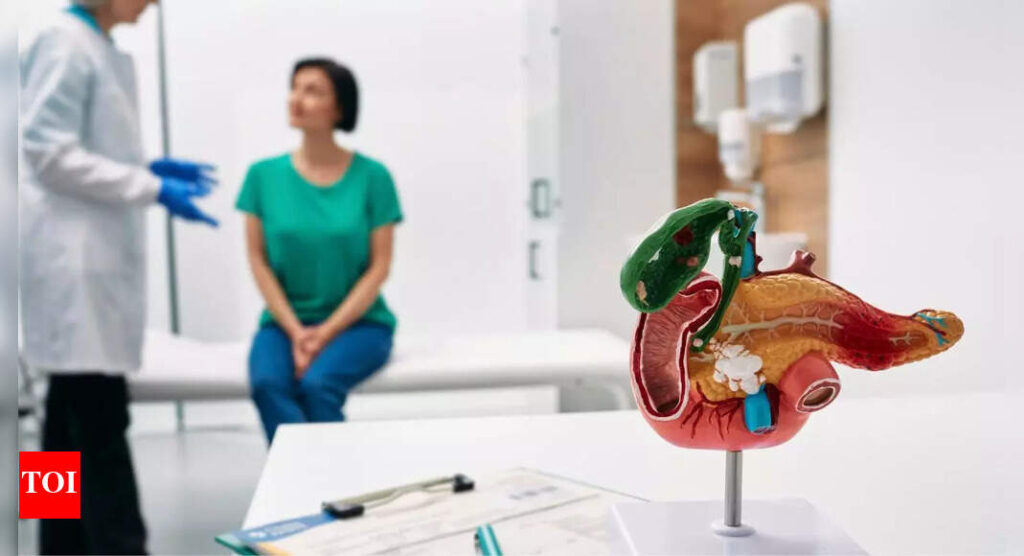
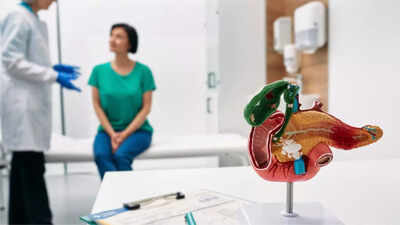
Gallbladder cancer is a rare but serious type of cancer where abnormal cells in the gallbladder grow out of control. The gallbladder, a small organ under the liver, stores bile to help digest food. Early stages often have no symptoms, making it difficult to detect. When symptoms appear, they can be similar to other conditions, also leading to delayed diagnosis. But if detected early, the chances of a cure are promising. However, most cases are diagnosed at a later stage, when the cancer has spread beyond the gallbladder, resulting in a poorer prognosis.Understanding the causes, risk factors, and symptoms is crucial for early detection and treatment. It can help people become aware of its warning signs and make informed health decisions.
What is gallbladder cancer?
Gallbladder cancer is a rare type of cancer that originates in the gallbladder, a small organ located beneath the liver that stores bile to aid in digestion. Gallbladder cancer often goes undetected in its early stages because it may not cause noticeable symptoms. When symptoms do appear, they can be similar to those of more common conditions, making it challenging to diagnose. The gallbladder’s location deep within the body also makes it easier for the cancer to grow without being detected, contributing to delayed diagnosis and treatment.
Where does gallbladder cancer spread?
Gallbladder cancer typically spreads in the following order, according to the Cleveland Clinic reports: From the inner layer to the outer layers of the gallbladder.To the nearby lymph nodes.To adjacent organs, such as the liver and bile ducts.Through the lymphatic system or bloodstream, it can further spread to other organs in the body (metastatic gallbladder cancer).
How common is gallbladder cancer ?
As per the Cleveland Clinic, gallbladder cancer is relatively rare, affecting about 2 people per 100,000 in the US. However, its incidence varies globally, with higher rates in countries like India, Japan, Korea, Poland, and certain South American nations, likely due to a greater prevalence of risk factors such as gallstones in these regions.
What causes gallbladder cancer?
The exact cause of gallbladder cancer is unclear, but according to MayoClinicreports, it’s known to begin when healthy gallbladder cells undergo DNA changes. Normally, DNA instructs cells to grow, multiply, and die at a set rate. However, in cancer cells, DNA changes lead to rapid cell growth and uncontrolled division. These abnormal cells don’t die as they should, resulting in an excessive number of cells. These cancer cells can form a tumor, invade nearby tissue, and eventually break away to spread to other parts of the body (metastatic cancer). Most gallbladder cancers are adenocarcinomas, originating in glandular cells lining the gallbladder’s inner surface.
Symptoms of gallbladder cancer
Symptoms of gallbladder cancer, as reported by MayoClinic, are:
- Abdominal pain, typically in the upper right side
- Belly bloating
- A palpable mass in the abdomen
- Unexplained weight loss
- Jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes), although this often indicates advanced cancer.
Note that gallbladder cancer may not exhibit symptoms in its early stages. Jaundice may be less noticeable on darker skin tones.
The stages of gallbladder cancer
According to the Cleveland Clinic, the stage determines the extent of cancer spread, with higher numbers indicating more widespread disease. The stages of gallbladder cancer are: Stage 0 (Carcinoma in situ): Abnormal cells are in the inner layer of the gallbladder.Stage 1: Cancer is in the mucosal layer and may reach the muscle wall.Stage 2: Cancer has spread to the connective tissue layers beyond the muscle layer.Stage 3: Cancer has spread to the liver, nearby organs, or outer layer of the gallbladder, and possibly to nearby lymph nodes.Stage 4: Cancer has spread to multiple lymph nodes, blood vessels, or distant organs.
Risk factors for gallbladder cancer
According to MayoClinic, these factors can increase the likelihood of developing gallbladder cancer
- Female sex, possibly due to higher estrogen levels.
- Increasing age, with most cases occurring after 65.
- History of gallstones, especially larger ones.
- Other gallbladder conditions, such as:
– Polyps – Infections – Chronic inflammationInflammation of the bile ducts (primary sclerosing cholangitis).
Can gallbladder cancer be prevented?
According to the Cleveland Clinic reports, gallbladder cancer can’t be guaranteed to be prevented, but reducing risk factors may help lower the risk. This can include maintaining a healthy weight with the guidance of a healthcare provider. However, even with these efforts, there’s no certainty that cancer can be prevented.Also read | Early or premature menopause: Causes, symptoms, risks and more