Table 1: Key Observations on HS -550320- Polyester Staple Fibres and trade statistics for CY 2024
South Korea leads US polyester staple fibre (PSF) imports, benefiting from zero tariffs under KORUS FTA and a strong logistics index.
Thailand and India remain competitive but face a 4.3 per cent tariff, impacting pricing.
China’s market share is weakening due to rising tariffs, now at 24.3 per cent, increasing costs.
Trade policies and cost structures will shape future market dynamics.
Source: TradeMap and F2F Analysis; *Effective from 4th March, 2025
Note: RCA – Revealed Comparative Advantage; UVR – Unit Value Realisation; LPI – Logistic Performance Index
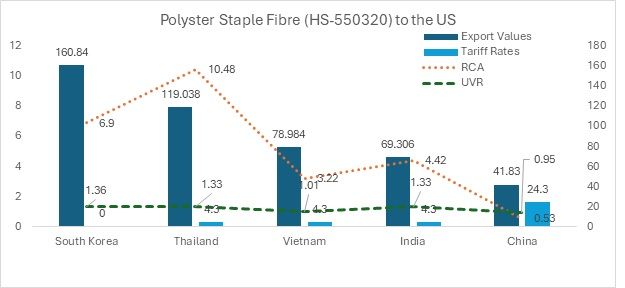
South Korea: Market leader with zero-tariff advantage
South Korea dominates the US PSF import market, with exports totalling $160.84 million, significantly outpacing its competitors. Benefiting from a zero-tariff rate under the KORUS (Korea-US) FTA, South Korea enjoys a strong pricing advantage. With a high RCA of 6.90 and a competitive unit price of $1.36/kg, it remains the most strategically positioned exporter of PSF to the US.
Thailand: Strong exporter with high trade value
Thailand ranks second in PSF exports to the US, with shipments totalling $119.04 million. It boasts a strong RCA of 10.48 and a highly competitive unit price of $1.33/kg. However, a 4.3 per cent tariff limits its price advantage, making it less competitive than South Korea, which benefits from a zero-tariff rate under the KORUS FTA.
Vietnam: Growing exporter with moderate competitiveness
Vietnam ranks third in PSF exports to the US, with a total export value of $78.98 million. It holds an RCA of 3.22, reflecting a moderate comparative advantage in PSF production and trade. However, like Thailand and India, Vietnam faces a 4.3 per cent MFN tariff, impacting its price competitiveness in the US market. Despite this, its unit price remains among the lowest among the top five exporters, second only to China.
India: Emerging player with similar competitiveness to Thailand
India ranks fourth in PSF exports to the US, with a total export value of $69.31 million. It holds a solid RCA of 4.42 and a competitive unit price of $1.33/kg, matching Thailand’s and highlighting its growing strength in PSF manufacturing. While the 4.3 per cent tariff impacts price competitiveness, India’s cost-efficient production helps partially offset this disadvantage.
China: Weakening market position due to lower RCA and tariffs
Despite being a global textile powerhouse, China’s PSF exports to the US remain relatively low at $41.83 million. With the lowest RCA (0.53) among top exporters, its ultra-low unit price of $0.95/kg reflects an emphasis on cost-driven exports but also signals declining competitiveness in this segment. The 4.3 per cent MFN tariff further weakens its position against tariff-exempt South Korea and other cost-effective suppliers.
Tariff Impact: With the first tariff imposition on February 4th, 2025, the tariff rate increased to 14.3 per cent. This rise in the tariff burden would lead to an increase in the UVR as production and export costs escalate. As a result, the UVR would likely increase to around $1.05/kg, reflecting the growing challenges posed by the higher tariffs. The increase in the UVR shows that the products are becoming more expensive, which could make them less competitive for price-sensitive consumers.
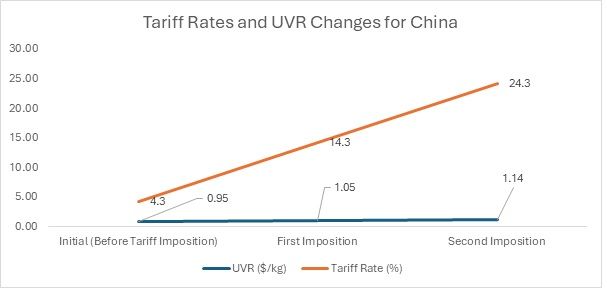
In the second tariff imposition, effective from March 4th, 2025, the tariff rate rose further to 24.3 per cent. This substantial increase would push the UVR to approximately $1.14/kg or higher. The higher tariff burden will continue to raise costs, further diminishing the cost-effectiveness of the products. Post imposition of tariffs, China will lose its advantage of being a low-cost supplier of polyester staple fibres.
Key observations & outlook
South Korea leads the US PSF import market, leveraging zero-tariff access under the KORUS FTA and the highest Logistics Performance Index (LPI) to maintain a dominant position.
Thailand and India remain strong competitors, but the 4.3 per cent tariff adds a cost disadvantage, limiting their pricing edge despite their competitive unit prices. Vietnam continues to expand its presence but lacks a strong comparative advantage compared to the top exporters.
China’s exports are declining, primarily due to reduced competitiveness and trade restrictions. If an additional 20 per cent tariff is imposed, China could face further setbacks, ceding market share to more cost-effective suppliers and having rivals with respect to price.
Trade agreements play a crucial role in shaping market dynamics, with South Korea benefiting the most from free trade arrangements. Meanwhile, Thailand and Vietnam share comparable LPIs, influencing their logistical efficiency.
Going forward, trade policies, cost structures, and supply chain resilience will be key factors in determining market shifts, with emerging players poised to gain ground in the evolving PSF landscape.
Fibre2Fashion News Desk (NS)

