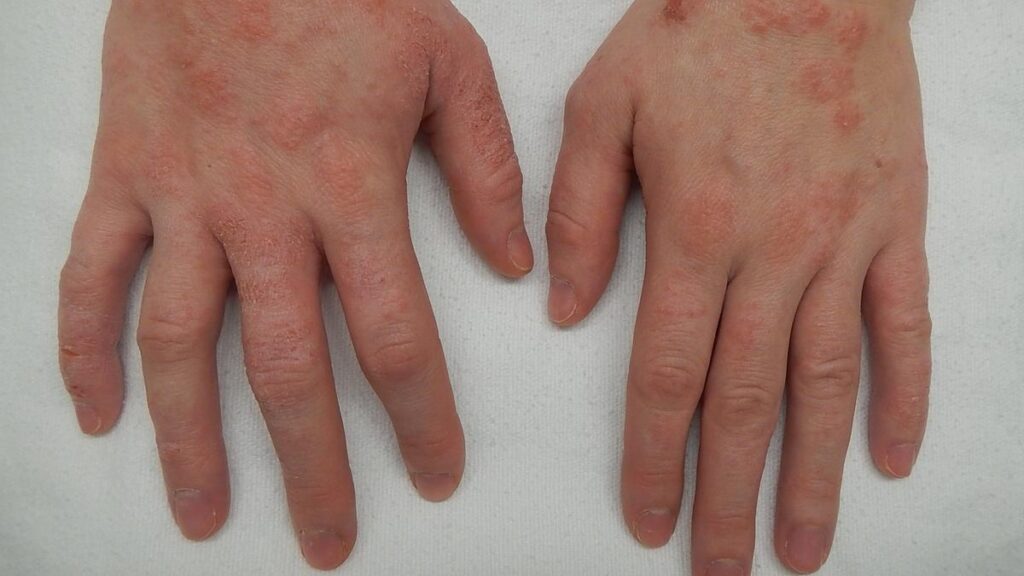
Eczema exists as multiple skin conditions that present different symptoms from distinct causes. Photograph used for representational purposes only
| Photo Credit: James Heilman, MD, CC BY-SA 4.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0>, via Wikimedia Commons
Eczema is a widespread skin disorder that induces skin inflammation while creating dryness and producing an intense itching sensation in millions of patients every year, globally.
Each case of eczema however, has individual characteristics. Different forms of eczema present distinct symptoms while requiring individual treatment methods, because each type behaves differently. The identification and treatment of eczema can become complicated because its appearance varies between different skin tones. Here we explore diverse types of eczema types, while analysing their skin tone presence and distinguisheing between eczema and other skin problems before investigating available treatment options.
Types of eczema
Eczema exists as multiple skin conditions that present different symptoms from distinct causes. The most common types include:
Atopic Dermatitis: Atopic Dermatitis functions as the primary type of eczema due to its development from inherited characteristics as well as allergic processes. Young children typically develop this skin condition, which sometimes becomes chronic during the adult years. Its symptoms include: itchy skin, inflammation, and redness. This condition can be kept under control by using ceramide-rich moisturizers, a healthy diet (avoiding foods that can trigger atopy), and a well-balanced lifestyle. All these measures can help improve internal immunity.
Dyshidrotic Eczema: A stressed person with allergic issues being exposed to metal that causes allergies may face this skin condition. Symptoms include itchy blisters on one’s feet and hands.
Contact Dermatitis: Getting exposed to harmful elements in the environment may cause this condition. This condition has two types under it: allergic contact dermatitis, which is caused by a reaction to allergic elements from metals, cosmetics, etc. and irritant contact dermatitis, which is caused as an immediate response to ingredients present in acids, soaps, detergents, or cleaning agents.
Nummular Eczema: A prolonged skin condition, with a coin-like appearance of scaly patches, causing itchiness, and usually appearing on the arms and legs when the skin becomes dry, or when there is an infection. This condition may show up and prevail till diagnosed.
Stasis Dermatitis: Some individuals have very little to poor blood circulation in their legs, and that is when one suffers from this skin condition. This condition has symptoms such as the skin starting to itch and becoming dry and red. Hence, it is advisable to keep the legs elevated while resting and avoid prolonged standing or sitting.
Seborrhoeic Dermatitis: If there are symptoms like patchy, red, fungal-like formations and white flakes around the glands that produce oil in the body, then these are indications of this non-contagious skin condition.

The importance of a correct diagnosis
The appearance of eczema differs across skin tones, often leading to incorrect diagnoses, frequently in in individuals with dark skin tones. Eczema shows up with red and inflamed symptoms in people with light skin tones, while appearing purple, grey, or brown with those who have dark skin tones.
Another issue is that several other skin conditions have symptoms similar to those of eczema, making it difficult to differentiate eczema from other skin conditions.
Here is a guide to differentiating between eczema and other skin conditions:
Psoriasis vs. Eczema: Dry and itchy skin shows up in both conditions. Eczema demonstrates more inflammation, whereas psoriasis shows evident silvery scales and clear borders around areas that are affected.
Fungal Infections vs. Eczema: People with fungal infections experience specific border characteristics that tend to appear in ring-shaped patterns, unlike the diffuse spreading observed in eczema.
Rosacea vs. Eczema: Eczema shows up across the body instead of only on the face, whereas rosacea makes the skin red, causing blood vessels to become visible.
What is the treatment?
The management of eczema requires adopting different lifestyle choices and getting medical interventions when needed, as well as proper skin care.
Topical steroids help control eczema inflammation, although they have the side effect of skin thinning. Non-steroidal alternatives are also available for treatment. The application of moisturisers helps prevent flare-ups of eczema, while natural oatmeal baths can bring relief. Implementing stress management practices with trigger avoidance also helps control eczema symptoms.
Medical research continues to progress in this field, with the development of a promising biologic drug Dupixent.
Different kinds of eczema have unique presentations and treatment plans. Correct diagnosis and appropriate management require physicians to differentiate between different types of eczema as well as recognise how they manifest on diverse skin tones and distinguish them from other related conditions. Patients must visit a dermatologist who can provide them with the right type of information and treatment.
(Dr. Sowmya Dogiparthi is a consultant dermatologist/cosmetologist at Apollo Spectra Hospitals, Chennai.)
Published – March 25, 2025 02:21 pm IST